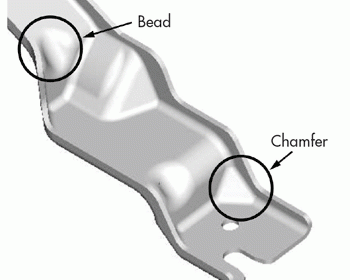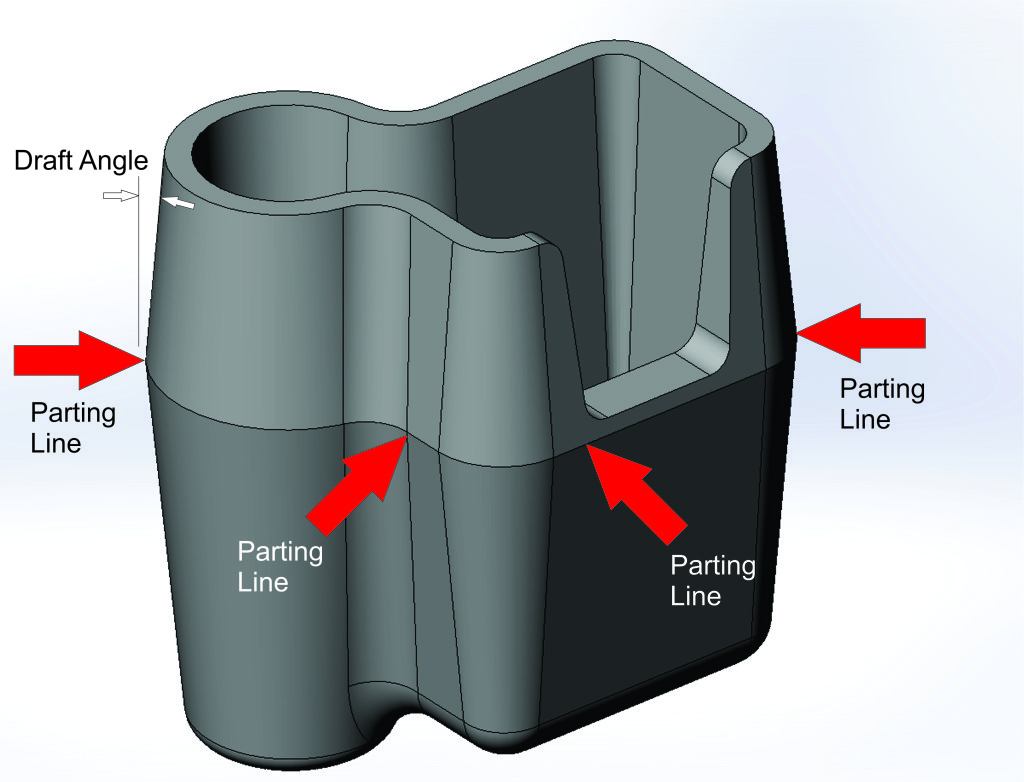
Designing plastic parts is a little different from designing metal parts. There are many things that must be carefully considered and planned for. Plastic parts can be made in many ways: injection molding, thermoforming, extrusion, blow molding, even casting. For the sake of brevity, this article will focus on one type: injection molding. If you’ve ever built a plastic model kit, you’ve seen and know at least something about injection molding. It is a process where heated (molten) plastic is […]
Tags: Plastic Parts